“Sweden has one of the highest rates of type 1 diabetes among children and adolescents globally. The incidence continues to rise, especially among teenagers, highlighting the need for increased awareness and early intervention”- Diabetes Journals
In Sweden, more and more people are getting diabetes. I was surprised when I learned how common it is. A lot of people in Sweden are living with this disease. This is part of a bigger trend happening around the world. It makes me think about things like food, lifestyle, and even genetics.
Diabetes in Sweden is something we need to talk about. I want to share what I found out by looking at the numbers, the risks, and what Sweden is doing to fight this disease. It’s important to understand how this affects Sweden so we can also see how it’s a bigger problem for everyone today.

Credit: news.cision.com
Diabetes In Sweden: A Snapshot
Diabetes is a significant health issue in Sweden. The prevalence of diabetes, especially type 1, has risen sharply in recent years. This trend indicates a growing concern about diabetes management and prevention in the country.
Diabetes is a growing health concern in Sweden, affecting a significant portion of the population. Understanding its prevalence and the factors influencing its rise can provide valuable insights. This snapshot aims to highlight current statistics and draw comparisons with neighboring Finland to shed light on the diabetes landscape in Sweden.
Current Statistics
As of recent estimates, approximately 5% of the Swedish population lives with diabetes. This figure translates to around 500,000 individuals, with the majority having Type 2 diabetes. – Type 1 diabetes is also a significant concern, particularly among children. Sweden has one of the highest incidences of Type 1 diabetes in the world, with around 40 new cases per 100,000 children diagnosed annually. The rise in diabetes cases can be attributed to various factors, including lifestyle changes, diet, and genetics. While Sweden boasts a robust healthcare system, the increasing prevalence of obesity and sedentary lifestyles poses challenges.
Comparative Analysis With Finland
When comparing diabetes statistics with Finland, the differences are striking. Finland has a slightly higher prevalence of Type 1 diabetes, with around 60 cases per 100,000 children diagnosed each year. – In terms of Type 2 diabetes, Finland shows similar trends, but the overall rates are marginally lower than in Sweden. Both countries face common risk factors, yet Finland’s proactive health initiatives may contribute to its lower Type 2 diabetes rates. Reflecting on these statistics, what can we learn about managing diabetes better in Sweden? Addressing lifestyle changes early could be key. Understanding these comparisons can help shape public health strategies and improve outcomes for those affected.
Factors Influencing Diabetes Rates
Diabetes rates in Sweden are influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors helps to shed light on the situation. Two main areas stand out: genetic predisposition and lifestyle choices. Each plays a significant role in diabetes prevalence.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors contribute significantly to diabetes rates. Family history often increases the risk. Certain genes make individuals more susceptible to Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
In Sweden, a higher incidence of Type 1 diabetes is observed. This autoimmune disease often develops in childhood. Genetic links to this condition are strong. Studies show that siblings of affected individuals have a higher risk.
Lifestyle And Dietary Habits
Lifestyle choices greatly affect diabetes rates in Sweden. Diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. High sugar and processed foods contribute to obesity. This is a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes.
Physical activity levels also impact diabetes prevalence. Sedentary lifestyles are becoming more common. Regular exercise can help maintain healthy weight and insulin sensitivity.
Swedes traditionally follow a balanced diet. However, modern eating habits are shifting. Increased consumption of fast food and snacks poses risks. Awareness of healthy lifestyle choices can help manage diabetes rates.
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence
Diabetes affects many people in Sweden. The two main types are Type 1 and Type 2. Each type has different causes and impacts. Understanding their prevalence helps highlight the issue.
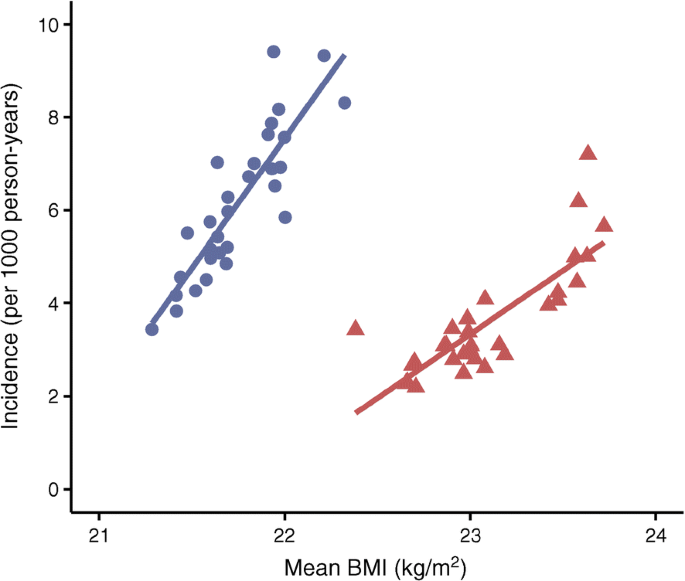
Childhood-onset Diabetes Trends
Sweden has a high rate of childhood-onset diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is the most common form in children. Recent studies show this number continues to rise. Each year, thousands of children are diagnosed. Factors like genetics and environment play a role.
Sweden’s diabetes registry tracks these cases closely. It helps researchers understand trends over time. The rise in childhood diabetes cases is alarming. Efforts to manage and prevent this condition are crucial.
Adult-onset Diabetes Statistics
Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults. Many adults in Sweden face this diagnosis. The rise in obesity and sedentary lifestyles contribute to this trend. Statistics show a steady increase in cases.
Older age groups are particularly affected. Lifestyle choices often lead to this type of diabetes. Awareness and education are key to prevention. Regular health checks can help catch it early.
Credit: link.springer.com
Impact Of Immigration On Diabetes
The relationship between immigration and diabetes is a complex and evolving topic in Sweden. As new populations settle in the country, their health outcomes often differ from the native population. Understanding how migration impacts diabetes prevalence can shed light on public health strategies and the need for tailored healthcare services.
Diabetes Among Migrants
Migrants often face unique challenges that can influence their risk of developing diabetes. Cultural differences in diet, lifestyle, and access to healthcare can play a significant role. For instance, a study found that migrants from the Middle East and North Africa often have higher rates of diabetes upon arrival in Sweden compared to native Swedes.
Many migrants may initially enjoy good health, but changes in diet and physical activity can quickly alter their health status. Adapting to a new environment can lead to a shift towards more sedentary lifestyles and processed foods, which are risk factors for diabetes.
Adaptation And Health Outcomes
The adaptation process can significantly affect health outcomes for migrants. Those who quickly integrate into the Swedish healthcare system often have better management of their health conditions. On the other hand, language barriers and lack of awareness about available resources can leave some migrants vulnerable.
Consider the experience of a Somali woman who moved to Sweden. Initially, she struggled with the language and was unaware of the importance of regular check-ups. After learning more about the healthcare system, she was able to manage her diabetes effectively, highlighting the need for accessible information for newcomers.
What can be done to improve health outcomes for migrants? Increased community outreach and educational programs can make a difference. By fostering connections and providing support, Sweden can help migrants lead healthier lives.
Diabetes Care In Sweden
Sweden has a strong focus on diabetes care. The country offers various support systems for patients. This ensures that those with diabetes receive the best possible treatment. Comprehensive healthcare policies play a vital role in managing diabetes effectively.
Healthcare System Support
The Swedish healthcare system is well-structured. It provides universal coverage for all citizens. This means that everyone has access to necessary medical care. Diabetes management is a priority within this system.
Patients receive regular check-ups and screenings. Healthcare professionals monitor blood sugar levels consistently. This helps in preventing complications related to diabetes. The system also emphasizes timely access to medication and insulin.
Patient Education Initiatives
Education is key in managing diabetes in Sweden. Various programs aim to inform patients about their condition. These initiatives cover topics like diet, exercise, and medication management.
Patients learn how to monitor their blood sugar levels. They receive guidance on making healthy lifestyle choices. Workshops and seminars are common. These help patients connect with others facing similar challenges.
Overall, patient education fosters a supportive community. It empowers individuals to take control of their health. This leads to better outcomes for those living with diabetes.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetes is essential. In Sweden, various strategies help reduce its risk. Public health campaigns play a significant role. Early detection programs also help catch diabetes early.
Public Health Campaigns
Sweden runs several public health campaigns. These campaigns educate people about diabetes. They promote healthy eating and regular exercise. Information is shared through social media, websites, and community events. The goal is to raise awareness about diabetes risk factors.
Campaigns target different age groups. Schools teach children about nutrition. Adults receive guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. These efforts aim to prevent obesity, a major diabetes risk factor.
Early Detection Programs
Early detection programs are vital in Sweden. They screen people for diabetes risk. Healthcare providers offer regular check-ups. These check-ups help identify early signs of diabetes.
In many areas, residents receive invitations for screening. Programs focus on high-risk groups, such as older adults. Early detection leads to timely treatment. This can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Future Projections For Diabetes
Understanding future projections for diabetes in Sweden is crucial. The number of diabetes cases is expected to rise. This increase poses challenges for healthcare and society. Early insights can help in planning effective strategies.
Research And Trends
Recent studies show a steady rise in diabetes cases in Sweden. Data indicates that nearly 5% of the population has diabetes today. This number may double in the next two decades. Obesity and sedentary lifestyles contribute significantly to this trend.
Researchers are focusing on prevention and management strategies. Programs aimed at lifestyle changes show promise. Continuous monitoring of blood sugar levels is gaining attention. The role of technology in diabetes management is also expanding.
Policy Implications
Rising diabetes rates require strong public health policies. The government must prioritize diabetes awareness campaigns. Access to healthcare and education about healthy lifestyles is essential.
Investments in community health programs can make a difference. Policies should support physical activity and healthy eating. Collaboration between healthcare providers and communities is vital for success.
Comparative Global Perspective
Understanding diabetes in Sweden requires a look beyond its borders. How does Sweden compare to other countries? What can global data reveal about this pressing health issue? These questions help paint a clearer picture of diabetes prevalence.
Sweden Vs Other Countries
Sweden has a notable diabetes rate. The prevalence stands at about 4.5%. This figure is lower than in countries like India and China, where diabetes rates soar. In India, nearly 8.9% of the population is affected. China follows closely with 11.4% of its population living with diabetes.
European countries show varying rates. Germany reports around 6% prevalence. This is higher than Sweden but lower than countries like France, which is at 7.2%. Scandinavian neighbors, like Finland, have higher rates too, often exceeding 5%.
Access to healthcare plays a role. Sweden’s robust healthcare system supports diabetes management. Other countries may lack such resources. This disparity affects both diagnosis and treatment. It highlights the importance of local healthcare policies.
Lessons From Global Data
Global diabetes data reveals significant trends. Countries with high obesity rates often report higher diabetes prevalence. Lifestyle choices impact health. Physical inactivity and poor diet contribute to rising cases worldwide.
Education is another key factor. Regions with effective health education see lower diabetes rates. Awareness campaigns can change public perception and behavior. Countries that prioritize health education often experience better outcomes.
Lastly, early diagnosis is crucial. Countries with regular screening programs catch diabetes cases sooner. This can lead to better management and outcomes. Sweden’s proactive approach serves as a model for others.

Credit: www.easd.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Diabetes A Problem In Sweden?
Diabetes is a significant health issue in Sweden. The country has one of the highest incidences of childhood-onset diabetes globally. Growing obesity rates and lifestyle factors contribute to increasing diabetes prevalence among adults as well. Awareness and management efforts are ongoing to address this health challenge.
Which Country Is Highest In Diabetes?
China has the highest number of diabetes cases globally, followed by India and Pakistan. These countries report significant diabetes prevalence, reflecting a growing health concern. Other nations with notable diabetes numbers include the United States, Brazil, and Russia.
What European Country Has The Most Diabetes?
Turkey has the highest diabetes prevalence in Europe, with around 14. 8% of its population affected. Other countries, like Germany and the UK, also report significant rates. Awareness and lifestyle changes are crucial to managing diabetes effectively in these regions.
Where Is Diabetes Least Common In The World?
Diabetes is least common in countries like Haiti, where lifestyle factors and genetic predispositions contribute to lower rates. Additionally, regions with traditional diets and active lifestyles, such as rural areas in Africa, also show lower diabetes prevalence.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a significant health issue in Sweden. The increasing rates affect many people. Awareness and education are crucial for prevention. Regular check-ups can help catch diabetes early. Healthy lifestyle choices play a vital role in managing this condition. Communities need to support those living with diabetes.
Together, we can work towards reducing its impact. Understanding diabetes is the first step in fighting it. Stay informed and take action for better health.






